When a conventional denture is not enough for your patient—due to uncomfortableness, looseness, bite force, or other factors—and the patient needs dentures that are bolstered by an implant you have two choices implant-supported or implant-retained dentures. Firstly, ensure the patient has a measured amount of bone in their jaw to accommodate and support implant dentures. Then, below, explore the characteristics, and pros and cons of two types of denture prosthetics: implant-supported and implant-retained dentures.
What are implant-supported dentures?
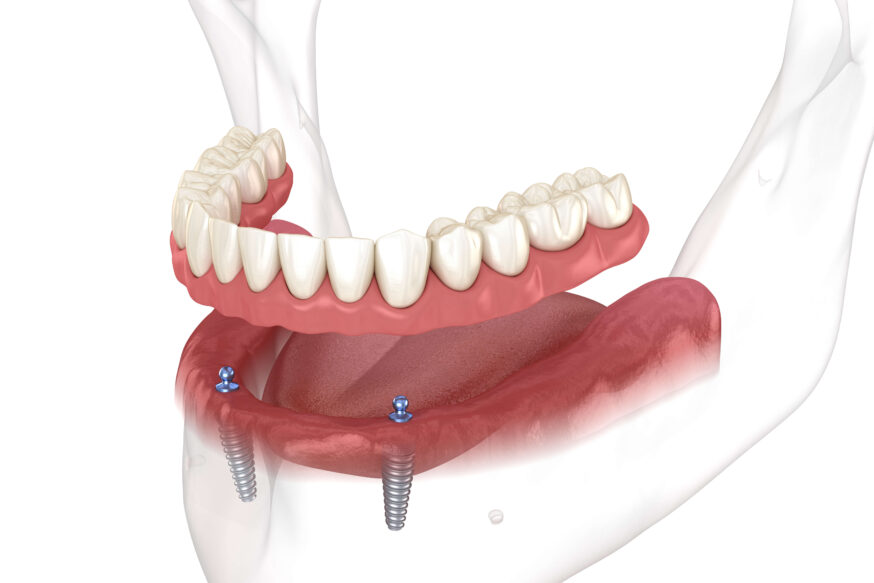
Implant-supported dentures sometimes referred to as overdentures, or removable implant dentures, function by snapping into placed dental implants.
Pros: Implant-supported dentures do not rely on suction to stay in place. They are more solid and stable because they are firmly attached to implants, keeping the dentures in place.
Cons: Over time, implant rings can wear down and require replacement.
Implant-supported dentures are removable and so they need to be removed at bedtime and placed in a denture-cleaning solution. The patient will need to clean their removable implant dentures and the area around the implants before bedtime. Because of their detachment, implant-supported dentures can become dislodged if the patient consumes certain types of foods.
The two types of implant-supported dentures: bar-retained and ball-retained.
Bar-retained dentures
Bar-retained dentures consist of a thin metal bar that follows the curve of the jaw, which is attached to two to five implants. Clips are fitted to the bar, the denture, or both.
Ball-retained dentures
Each implant holds a metal attachment that fits into an attachment on the denture. The attachments on the implants are usually ball-shaped and designed to fit into sockets on the denture.
Implant-supported denture cost
Implant-supported dentures are more expensive than conventional dentures due to implant surgery, implant cost, and chair time.
What are implant-retained dentures?
Implant-retained dentures, sometimes called all-on-4 or all-in-6 dentures, are dentures that are fastened to four or six dental implants embedded into the jawbone per arch.
Implant-retained dentures come in two types:
- Titanium bar with acrylic-rounded and denture teeth
- Full zirconium, continuous piece denture
Pros: Implant-retained dentures are securely screwed into place. The patient isn’t required to remove their dentures at night. Because there is no acrylic next to the palate, it makes the implant-retained denture more comfortable for the patient. Implant-retained dentures are stronger so the patient can bite and chew a wider variety of foods. All-on-4 dentures rarely become dislodged.
The zirconium implant-retained denture is made of one material and is considered stronger than the titanium bar version. Also, the zirconium option is usually more aesthetically pleasing.
Cons: With the titanium bar denture the acrylic may separate from the titanium bar. Implant-retained dentures are more difficult for the patient to clean. They are required to clean their dentures each night (suggested) using a Waterpik, floss threader, and mouthwash, which can take a considerable amount of time.
Lastly getting implant-retained dentures is a more invasive procedure for the patient.
Implant-retained denture cost
Implant-retained dentures are the more expensive option of implant dentures. Although, the titanium bar option may be more affordable for patients.
An overview of implant denture workflow
1. Pre-prosthetic surgery
The dentist extracts any decayed or damaged teeth and performs bone grafting if necessary. Patients may need to heal for several weeks before implants are placed. The dentist gives the patient a healing denture to wear during recovery.
2. Dental implant placement
A dental surgeon places the dental implants into the jawbone. It takes up to six months for the implants to fuse with the jawbone. The patient wears the healing denture while waiting for the implants to integrate.
3. Dental impressions
When the dental implants have healed, the dentist takes impressions of the upper and lower dental arches and sends the impressions to the lab to design the new dentures.
4. Denture placement
The dentist attaches the new dentures to the implants. They show the patient how to clean and care for their dentures.
Implant-supported vs implant-retained dentures: Which is best for your patient?
Factors to consider when prescribing dentures include the patient’s health, diet choices, lifestyle and budget. Talking with your patients about the available options and the pros and cons of each will ensure your patients will be happy with their choice and their smile, for years to come.
Which patients are best suited for implant-supported dentures?
Patients that have a moderate budget and are willing to undergo surgery to take advantage of a more comfortable, stable and removable denture. Implant-supported dentures are usually recommended for patients with a high upper smile because they hide the space where the denture base meets the gum line.
Which patients are best suited for implant-retained dentures?
A patient who loves to eat steak and other chewy foods may prefer the implant-retained option. Also a patient with a healthy budget who desires the most comfortable, strong, and aesthetically pleasing denture option is right for implant-retained dentures.
Sources